
- #Mac command line disk utility how to
- #Mac command line disk utility mac os
- #Mac command line disk utility plus
- #Mac command line disk utility free
- #Mac command line disk utility windows
The syntax is going to look like this: Diskutil eraseDisk JHFS+ Empty /dev/disk5s2
#Mac command line disk utility mac os
Let’s say the disk I want to erase has “/dev/disk5s2” as its identifier and I’m going to use Mac OS Extended Journaled (JHFS+) as the system format type and name it “Empty”. This is the syntax we need: Diskutil eraseDisk FILESYSTEM DISKNAME DISKIDENTIFIER Then pick a name and a system format type. Once you have found the proper drive to erase, just copy its identifier so you can use it for the next command. In order to repair a disk using an fsck command, you need to log in into the Mac using a single user mode. It can easily run on the command line to perform an HFS disk repair for Mac. This is going to list all the mounted drives on your Mac. Generally, the command runs automatically at the boot time, but, the command can also be manually run in case there is any problem with the file system. Start off by running the following command in the command line: Diskutil list Here I'll show you how you can erase and format a disk using the command line. To do that, the only thing you need is a bit of precise syntax to make sure that you are erasing the proper disk. But some Mac users might need to erase them from the command line on Mac OS. The first thing to try is to restart your Mac and press Command and R again as you boot up.

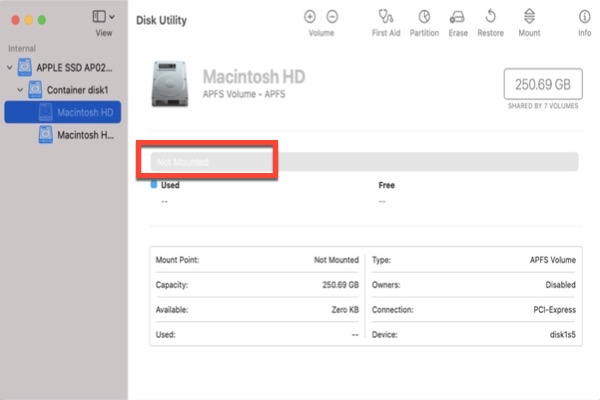
On the far right, you’ll see an IDENTIFIER column that column contains the identifier that diskutil needs.Most users use Disk Utility to erase a disk or hard drive. Just use diskutil list to see a list of all drives and partitions.
#Mac command line disk utility free
Consider using APFS encryption (FileVault).īut how do you figure out what to list for device, which is the disk (or partition) that has the free space you’re trying to securely erase? diskutil can provide that information, too. Strongly-encrypted data can be instantly "erased" by destroying (or losing) the key (password), because this renders your data irretrievable in practical terms. The modern solution for quickly and securely erasing your data is encryption. Modern devices have wear-leveling, block-sparing, and possibly-persistent cache hardware, which cannot be completely erased by these commands. NOTE: This kind of secure erase is no longer considered safe.
#Mac command line disk utility plus
O 4 - Three-pass erase, consisting of two random fills plus a final zero fill. O 2 - Seven-pass erase, consisting of zero fills and all-ones fills plus a final random fill. Ownership of the affected disk is required. If you need to erase all contents of a partition but not its hosting whole-disk, use the zeroDisk or randomDisk verbs. Erasing freespace on a volume will leave your files intact, indeed, from an end-user perspective, it will appear unchanged, with the exception that it will have attempted to make it impossible to recover deleted files. Secure erasing makes it harder to recover data using "file recovery" software.Įrasing a whole-disk will leave it useless until it is partitioned again.
#Mac command line disk utility how to
Within the man pages, you’ll find the explanation for how to securely erase a disk’s free space using diskutil: secureErase level deviceĮrase, using a "secure" (but see the NOTE below) method, either a whole-disk (including all of its partitions if partitioned), or, only the free space (not in use for files) on a currently-mounted volume. To find out about diskutil in detail, type man diskutil at the Terminal prompt. Disk Management is buried several layers deep, so having a faster.
#Mac command line disk utility windows
A quick way to open the Disk Management utility in Windows is from the Command Prompt. As with the Disk Utility application, double (nay, triple) check your drives to make sure that either they are backed up or you absolutely positively do not need any of.
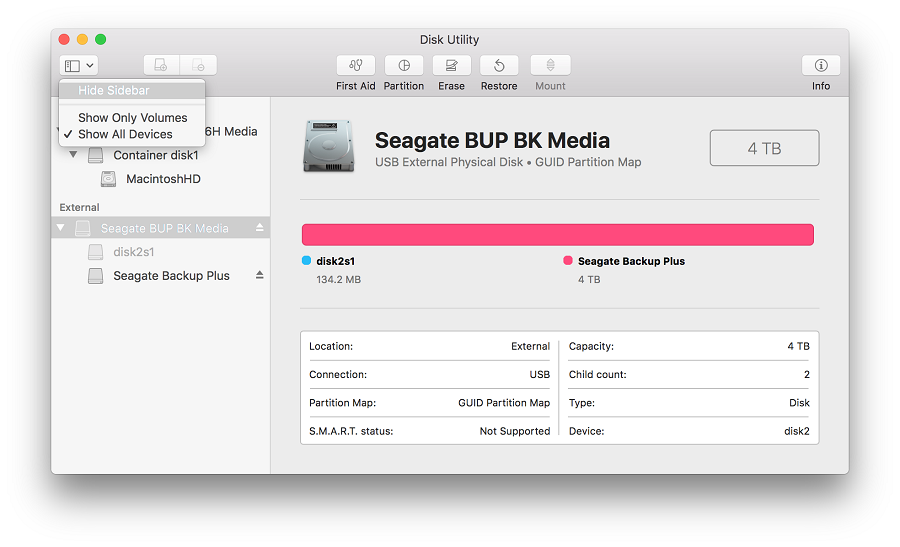
And beneath each disk you should see any containers and volumes on that disk. The sidebar in Disk Utility should now show each available disk or other storage device, beginning with your startup disk. Or, open Task Manager via Ctrl + Shift + Esc and go to File > Run new task. Now that you are looking at a command prompt on the target server use the diskutil command to prepare the hard drives for installation. Select your disk in Disk Utility Choose View > Show All Devices (if available) from the menu bar or toolbar in Disk Utility.

In Unix, all devices appear as part of the file system tree, and in macOS. Alternatively, press WIN + X and select Disk Management. Proceed with caution, and make sure your backups are current before you try any of the following.) There’s just one last bit of information you need to know to erase the free space on a hard drive from the command line. (Please note that, as with many Terminal commands, there’s a chance of Really Bad Things happening if you make a mistake with the following instructions. What if you want to do this from Terminal instead? In Terminal, a program named diskutil provides most of the features of macOS’s Disk Utility.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
